Gluten might seem like an innocent ingredient found in bread, pasta, and baked goods, but for some people, it can silently wreak havoc on their health. Because gluten sensitivity doesn’t always present obvious symptoms, many individuals remain unaware that their body is struggling to process it. Ignoring the signs can lead to long-term health complications. Let’s dive into 15 ways your body might be telling you that gluten is a problem.
1. Unexplained Fatigue and Brain Fog

Do you feel tired all the time, even after a full night’s sleep? Do you struggle to concentrate or experience moments of forgetfulness? These could be signs of gluten sensitivity. Gluten triggers inflammation in some individuals, which can lead to sluggishness, difficulty focusing, and a general sense of mental cloudiness.
2. Eyelash and Hair Loss
Losing more hair than usual? Even your eyelashes seem to be thinning out? Gluten intolerance can interfere with nutrient absorption, leading to deficiencies in iron, zinc, and biotin—key elements for strong, healthy hair. This deficiency can result in excessive hair shedding, brittle strands, and thinning eyelashes.
3. Digestive Discomfort (Bloating, Gas, Diarrhea, or Constipation)
Digestive issues are among the most common symptoms of gluten sensitivity. If you frequently experience bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or constipation after eating gluten-containing foods, your body may be struggling to break it down. Many people with undiagnosed gluten intolerance are mistakenly diagnosed with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
4. Chronic Headaches and Migraines
Headaches are common, but if you frequently suffer from migraines or severe headaches, gluten might be the culprit. Research suggests that gluten can trigger neurological inflammation, leading to frequent and intense headaches. If you’ve tried various remedies with no relief, cutting out gluten might be worth considering.
5. Sudden Weight Fluctuations
Gluten intolerance can lead to unexplained weight gain or weight loss. When your body can’t properly absorb nutrients, it may struggle to maintain a healthy weight. Inflammation caused by gluten can also interfere with metabolism, leading to unexpected changes in weight.
6. Hormonal Imbalances and PMS Symptoms
Women with gluten sensitivity often experience irregular menstrual cycles, severe PMS symptoms, or even fertility issues. Gluten can disrupt hormonal balance, affecting estrogen and progesterone levels. If you’ve been struggling with hormonal imbalances, it might be time to evaluate your diet.
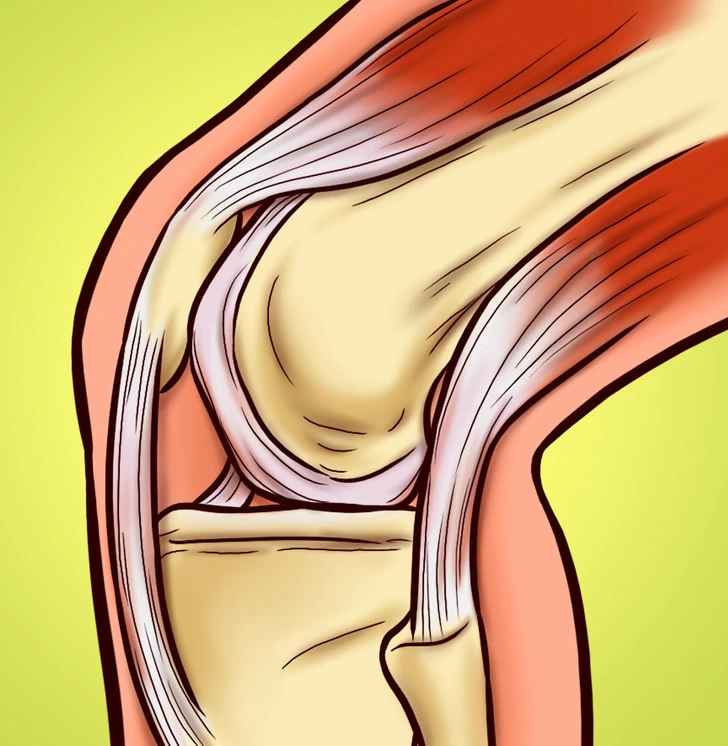
7. Joint and Muscle Pain
Do you often feel sore, even when you haven’t worked out? Gluten can contribute to systemic inflammation, causing joint stiffness, muscle pain, and even conditions resembling arthritis. If you notice joint discomfort after meals, gluten might be aggravating your symptoms.
8. Skin Rashes and Nail Problems
Gluten intolerance doesn’t just affect the inside of your body—it can also impact your skin. Conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis herpetiformis (a chronic rash associated with celiac disease) may worsen due to gluten consumption. Additionally, brittle nails or frequent breakage could be a sign of poor nutrient absorption.
9. ADHD-Like Symptoms and Difficulty Focusing
Gluten intolerance has been linked to neurological issues, including Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Many people with gluten sensitivity report struggling with focus, impulsivity, and difficulty maintaining attention. Studies suggest that eliminating gluten may help improve cognitive function in sensitive individuals.
10. Tooth Decay and Frequent Mouth Ulcers
Poor dental health can be a surprising indicator of gluten intolerance. Because gluten interferes with calcium absorption, individuals with sensitivity may experience weakened enamel, frequent cavities, and increased tooth sensitivity. Additionally, recurrent mouth ulcers or canker sores could signal an underlying gluten issue.
11. Iron Deficiency Anemia
Iron deficiency anemia, which causes fatigue, weakness, and pale skin, is commonly linked to celiac disease and gluten sensitivity. If your iron levels remain low despite taking supplements and eating iron-rich foods, your body may not be absorbing nutrients properly due to gluten-induced intestinal damage.

12. Anxiety, Depression, and Mood Swings
Did you know that your gut health directly affects your brain? Gluten can contribute to mood disorders by disrupting the gut microbiome and causing inflammation in the nervous system. Anxiety, depression, irritability, and mood swings can all be signs of an underlying gluten intolerance.
13. Autoimmune Diseases and Chronic Illnesses
Gluten intolerance is often linked to autoimmune disorders. Individuals with celiac disease are at a higher risk of developing conditions such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis. If you have an autoimmune condition, eliminating gluten might help reduce symptoms and flare-ups.
14. Tonsil Stones and Chronic Throat Issues
Though not widely recognized, many gluten-sensitive individuals report chronic tonsil stones, throat discomfort, or postnasal drip. If you frequently develop tonsil stones, consider testing for gluten sensitivity—it might be the missing link.
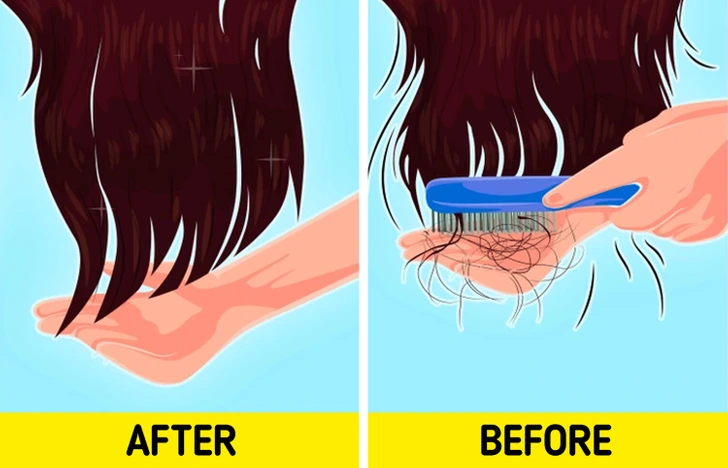
15. Persistent Hair Thinning and Bald Patches
Beyond just eyelashes, gluten intolerance can cause overall hair loss, including bald patches associated with autoimmune conditions like alopecia areata. Malabsorption of key nutrients needed for hair growth can lead to brittle hair, excessive shedding, and even premature graying.
What Should You Do If You Suspect Gluten Sensitivity?
If you experience multiple symptoms on this list, it might be time to investigate further. Here’s what you can do:
1. Get Tested
Ask your doctor for a gluten sensitivity or celiac disease test. A simple blood test can check for gluten-related antibodies. If results are inconclusive, an elimination diet can help determine if gluten is affecting your health.
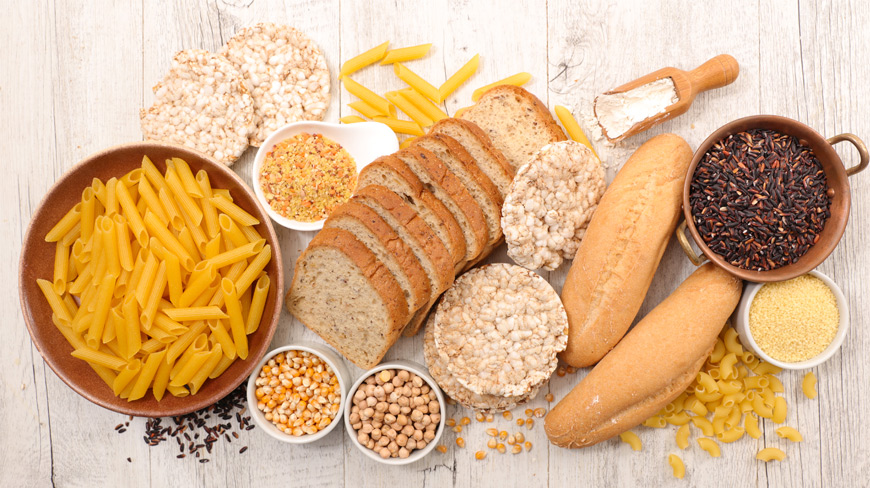
2. Remove Gluten from Your Diet
To see if gluten is the culprit, try eliminating it completely from your diet. This means avoiding:
- Wheat
- Rye
- Barley
- Bulgur
- Semolina
- Most processed and packaged foods
Look for “gluten-free” labels and focus on whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and gluten-free grains like quinoa and rice.

3. Monitor Your Symptoms
Keep a journal of your symptoms before and after eliminating gluten. Many people notice a drastic improvement in their energy levels, digestion, and overall well-being within weeks of going gluten-free.
Final Thoughts
Gluten sensitivity can manifest in surprising ways, from brain fog to brittle nails and everything in between. If you’ve been dealing with unexplained health issues, your diet might be the key to feeling better. Pay attention to your body’s signals—sometimes, the smallest dietary change can make the biggest difference!
Ever noticed a white coating on your tongue? That could be another hidden health warning. Stay tuned to find out what it means and how to treat it naturally


